In 2025, resolving technical SEO issues is critical for any business seeking top ranks, larger traffic, and boosted conversions. Whether you manage an e-commerce site, local business, SaaS platform, or publisher website, ignoring technical SEO errors can lead to crawlability problems, indexing failures, and visibility loss.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the most common technical SEO issues and how to fix them. We will look at what can go wrong, how to identify these problems using modern tools (including AI), and the steps you need to take to fix them. We will break this down into simple, easy-to-understand language so you can ensure your website is healthy and ready for growth in 2025.

What Are Technical SEO Issues?
Technical SEO issues are structural and backend problems that prevent search engines like Google from effectively crawling, indexing, and understanding your website. These include issues related to site architecture, speed, mobile optimization, security, and structured data.
Technical SEO vs On-Page vs Off-Page SEO

- Technical SEO: Enhancing the structure of your website to make it easier for search engines to crawl and index your content is known as technical SEO. It considers factors including server performance, XML sitemaps, HTTPS, structured data, and how quickly the website loads and functions on mobile devices.
- On-Page SEO: The main goal of on-page SEO is to optimize your website's content, including headers, internal linking, meta tags, multimedia, and keyword targeting. Its objective is to increase the relevance and value of your pages for search engines and users alike.
- Off-Page SEO: The main goal of off-page SEO is to establish authority and trust through actions that take place outside of your website. To increase your website's legitimacy in search engine results, this entails obtaining backlinks, controlling your online reputation, and utilizing social signals.
Why Fixing Technical SEO Errors Is Critical for Your Website?
If you disregard technical SEO issues, your website’s capacity to appear in search results may suffer significant damage. These issues may impact conversions, increase bounce rates, and decrease your chances of ranking.
Complications with technical SEO, such as sites that load slowly, broken links, or a lack of sitemaps, could hamper the development of your online presence.
Use cases:
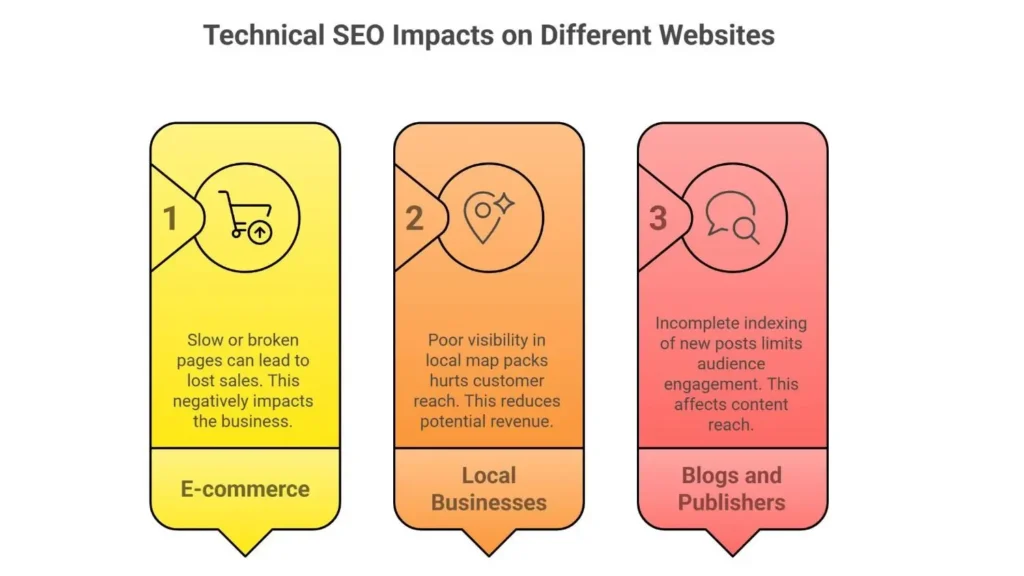
- E-commerce: Lost sales due to slow or broken pages.
- Local businesses: Poor visibility in local map packs.
- Blogs and Publishers: Incomplete indexing of new posts.
The Gatekeepers: Crawling and Indexing Problems
The most serious technical issues are the ones that stop Google from even seeing your site. If your site isn’t “indexed,” it doesn’t exist in Google’s library.
1. The Robots.txt Block
Every website has a file called robots.txt. Think of this file as the security guard at the gate of your digital house. It tells search engines which rooms they are allowed to enter and which ones are private.
A very common technical seo issue happens when a website owner accidentally tells the security guard to lock everyone out. This often happens during website development. Developers will block Google so the unfinished site doesn’t show up in search results. However, they sometimes forget to remove that block when the site goes live.
How to Fix It: You can check this by typing yoursite.com/robots.txt in your browser. If you see a line that says Disallow: /, you are blocking everything. You need to go into your website settings or ask your developer to remove that line immediately.
2. Missing or Messy XML Sitemaps
If your website is a book, the XML Sitemap is the table of contents. It is a file that lists every single page on your site that you want Google to find.
If you don’t have a sitemap, or if your sitemap is full of old links that don’t work anymore, Google has to guess where your pages are. This is inefficient and hurts your rankings.
How to Fix It: Most website platforms generate this automatically. You need to find your sitemap URL (usually yoursite.com/sitemap.xml) and submit it to Google Search Console. This is a free tool from Google that acts like a health monitor for your website. Submitting your sitemap is like handing the map directly to the driver.
3. The "Noindex" Tag Error
Sometimes, you might want to hide a specific page, like a “Thank You” page after a customer buys something. You do this using a “noindex” tag. A major error occurs when this tag is accidentally placed on important pages, like your homepage or your best blog posts.
How to Fix It: To troubleshoot technical seo issues like this, use a browser extension or an SEO audit tool. If you see a “noindex” tag on a page that you want people to find, you must go into your page settings and turn indexing back on.
The Need for Speed: Performance Issues
In 2025, patience is rare. If your website takes more than three seconds to load, most visitors will leave. Google knows this, so they prioritize websites that are fast and stable. These performance problems are common technical issues affecting seo performance.
4. Slow Page Loading Times
Websites become slow for many reasons. Usually, it is because the images are too big, the code is messy, or the server (where your website lives) is cheap and slow.
How to Fix It: Start by putting your website into Google’s “PageSpeed Insights” tool. It will give you a score and tell you exactly what is slowing you down.
- Compress Images: Large pictures are heavy. Use tools to shrink the file size without making the picture look blurry.
- Enable Caching: This saves a version of your website on the visitor’s computer so it loads faster the next time they visit.
- Clean up Code: If you use WordPress, remove plugins you aren’t using. They act like heavy backpacks slowing your runner down.
5. Mobile-Friendliness Failures
More people browse the internet on phones than on computers. Because of this, Google uses “Mobile-First Indexing.” This means Google looks at the mobile version of your site first to decide where to rank you. If your text is too small to read on a phone, or if buttons are too close together, you have a major technical error.
How to Fix It: You must use a “responsive design,” which means your website automatically changes shape to fit the screen it is on. Check your site on your own phone. If you have to pinch and zoom to read the text, you need to switch to a mobile-friendly theme immediately.
Structural Integrity: Links and Duplicates
Broken links and duplicate content create significant challenges for search engines attempting to crawl and index a website. This lack of structural integrity can impede efficient navigation, resulting in a suboptimal user experience and potentially lower search rankings.
6. Broken Links (404 Errors)
A 404 error happens when a user clicks a link, but the page is gone. It is frustrating for users and it wastes the “crawl budget” of search engine bots. If a bot hits too many dead ends, it might stop exploring your site.
How to Fix It: Fixing common technical seo issues like this requires scanning your site. You can use free tools or AI seo tools to find all the broken links.
- Update the link: If you just typed the URL wrong, fix the spelling.
- Redirect (301): If you deleted an old page, set up a “301 Redirect.” This automatically forwards anyone trying to visit the old page to a relevant new page.
7. Duplicate Content Confusion
This is one of the trickiest technical issues. It happens when the same content appears on different URLs. For example, http://yoursite.com and https://www.yoursite.com might look the same to you, but to a robot, they are two different pages with the exact same text. Google doesn’t know which one to rank, so it penalizes both.
How to Fix It: You need to pick the “master” version of the page and use a Canonical Tag. This is a small piece of code that tells Google, “Hey, I know there are copies, but this is the original one. Rank this one.”
Platform-Specific Challenges
Different website builders have their own unique quirks. Knowing which technical seo issues are most important often depends on what software you are using.
8. Technical SEO Issues with Shopify
Shopify is great for selling things, but what are the technical seo issues with shopify?
- Forced URL Structure: Shopify adds extra words to your links (like /products/ or /collections/), making them longer and harder to read.
- Duplicate URLs: One product might have different links depending on how a customer found it (e.g., through a collection page).
How to Fix It: You often need to edit the theme code to ensure Shopify points the “Canonical Tag” to the main product page, not the collection path. Installing specific SEO apps for Shopify can also help automate these fixes.
The Future: AI and Automation in 2025
As we move further into the digital age, fixing these problems is becoming easier thanks to Artificial Intelligence.
9. Can AI SEO Tools Help?
Absolutely. You might wonder, can ai seo tools help with technical seo issues? The answer is yes. Tools like Alli AI or even ChatGPT are changing the game.
- ChatGPT Technical SEO Issues Identification: You can copy pieces of your website code and ask ChatGPT, “Is there an error in this schema markup?” or “Write me a rule for my robots.txt file.” It acts like a coding assistant.
- How Does Alli AI Handle Technical SEO Issues?: Advanced tools like Alli AI can actually install themselves on your website and automatically fix code errors, optimize images, and create redirects without you having to write a single line of code. This is the future of fixing common technical seo issues—letting the software do the heavy lifting.
Security: The Trust Factor
Secure your website with HTTPS and an SSL Certificate now. Browsers label HTTP sites ‘Not Secure’, scaring visitors. Secure sites are a ranking factor, building trust and showing a padlock icon for data safety.
10. HTTPS and Security Warnings
If your website still uses “HTTP” instead of “HTTPS,” browsers will label it “Not Secure.” This scares visitors away. Secure websites are a ranking factor for Google.
How to Fix It: You need an SSL Certificate. Most web hosting companies give this away for free now. Once installed, your URL bar will show a padlock icon, telling users and Google that their data is safe.
How to Troubleshoot Technical SEO Issues: A Strategy
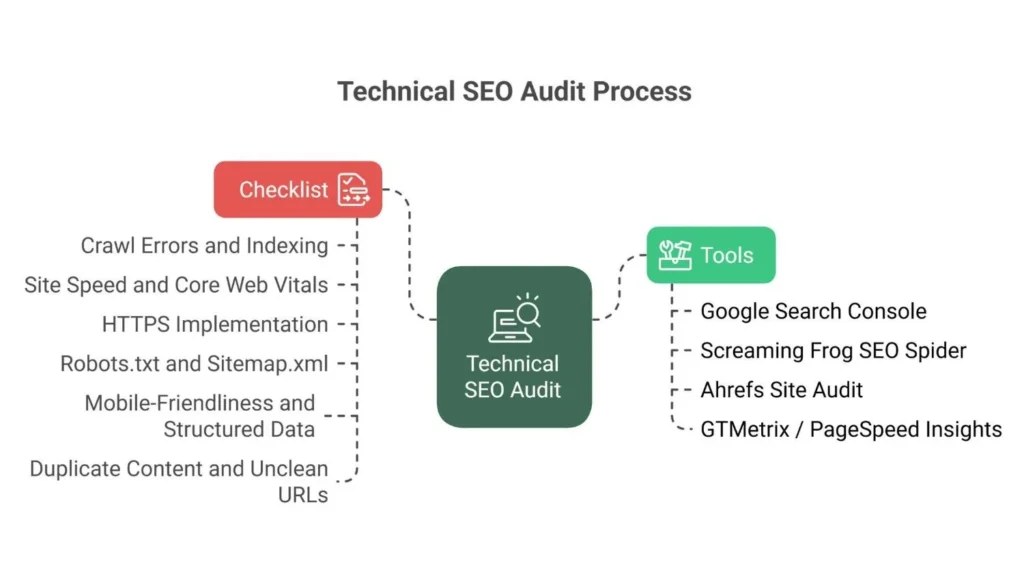
If you want to know how to fix seo issues systematically, follow this plan:
- Run an Audit: Use a tool (like Google Search Console, Ahrefs, or SE Ranking) to scan your website.
- Prioritize: Not all errors are equal. Which technical seo issues are most important? Always fix the ones that stop crawling (Robots.txt, Noindex) first. Then fix security (HTTPS), then speed, and finally content issues like broken links.
- Fix the Homepage First: If you are overwhelmed, learn how to fix seo errors on homepage first. The homepage is the most important page. If it is broken, the rest of the site suffers.
- Monitor: SEO is not a one-time job. New common technical seo issues 2025 will arise as technology changes. Check your site’s health once a month.
Geo SEO and Local Technical Optimization Tips

For businesses targeting local customers:
- Create and verify your Google Business Profile
- Embed maps and use local keywords on landing pages
- Use the LocalBusiness schema with geo-coordinates
- Ensure consistent Name, Address, Phone (NAP) across listings
- Submit geo-sitemaps for city-specific URLs in Search Console
Conclusion
Technical SEO might sound complicated, but it is just about making your website easy for robots to read and safe for humans to use. By addressing these Technical SEO Issues—from unlocking your site for crawlers to speeding up your images—you are building a strong foundation.
Remember, you don’t have to fix everything in one day. Start with the critical errors like crawling and security. Then, move on to performance and structure. With the help of new AI tools and a clear strategy, you can master techincal seo fixes and watch your traffic grow.A healthy website is a wealthy website, and a good digital marketing agency in lahore can help you achieve that.
FAQs
What are technical SEO issues?
They are backend problems that affect your site’s visibility in search engines, including slow speed, poor structure, and crawl errors.
How do I fix technical SEO errors on my website?
Conduct an SEO audit using tools like GSC, Screaming Frog, and Ahrefs. Fix broken links, add schema, and optimize speed and mobile usability.
Is technical SEO different from on-page SEO?
Yes. Technical SEO focuses on infrastructure and crawlability, while on-page SEO deals with content and meta data.
How often should I do a technical SEO audit?
Conduct a technical SEO audit quarterly, or monthly for large, frequently updated websites to maintain performance and search visibility.
Does technical SEO affect Google ranking?
In a word, yes. Google uses signals including mobile friendliness, security, speed, and structured data as ranking factors.